Debt Settlement vs Bankruptcy: Which Option Saves More Money in 2026?
Debt Settlement vs Bankruptcy: Which Option Saves More Money in 2026?
With inflation pressures, rising interest rates, medical bills, and record-high credit card APRs in 2026, millions of Americans are struggling with unsecured debt. If you’re overwhelmed by credit card balances, personal loans, medical collections, or wage garnishments, you may be considering two major debt relief options: debt settlement or bankruptcy.
Both strategies can reduce or eliminate debt — but they work very differently. The financial, legal, tax, and credit consequences vary significantly. Choosing the wrong option could cost you thousands of dollars and years of financial recovery.
This in-depth 2026 guide compares debt settlement vs bankruptcy across total cost, timeline, credit score impact, legal protection, tax consequences, asset risk, and long-term financial recovery — helping you determine which option truly saves more money.
Understanding Debt Settlement
Debt settlement is a negotiation process where you or a debt settlement company negotiates with creditors to reduce the total balance owed. Instead of paying 100% of the debt, you may settle for 40%–70% of the original balance.
How Debt Settlement Works
- You stop making payments to creditors.
- Funds accumulate in a dedicated account.
- Negotiators offer lump-sum settlements.
- Creditor forgives a portion of the debt.
This process typically applies to unsecured debt such as:
- Credit cards
- Personal loans
- Medical bills
- Private student loans (limited cases)
Understanding Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a federal legal process designed to eliminate or restructure debt under court supervision. The two most common consumer bankruptcy options in the United States are:
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy – Liquidation and discharge of unsecured debt.
- Chapter 13 Bankruptcy – Court-approved repayment plan over 3–5 years.
Bankruptcy immediately triggers an automatic stay, which stops collection calls, lawsuits, wage garnishments, and foreclosure proceedings.
Debt Settlement vs Bankruptcy: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Category | Debt Settlement | Chapter 7 Bankruptcy | Chapter 13 Bankruptcy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Cost | 15%–25% of enrolled debt | $1,500–$3,500 | $3,000–$6,000+ |
| Debt Reduction | 30%–60% | Most unsecured discharged | Partial repayment |
| Timeline | 2–4 Years | 3–6 Months | 3–5 Years |
| Credit Impact | Severe but temporary | Stays 10 years | Stays 7 years |
| Stops Lawsuits | No guarantee | Yes (automatic stay) | Yes |
| Tax Consequences | Possible 1099-C taxable income | No tax on discharged debt | No tax on discharged debt |
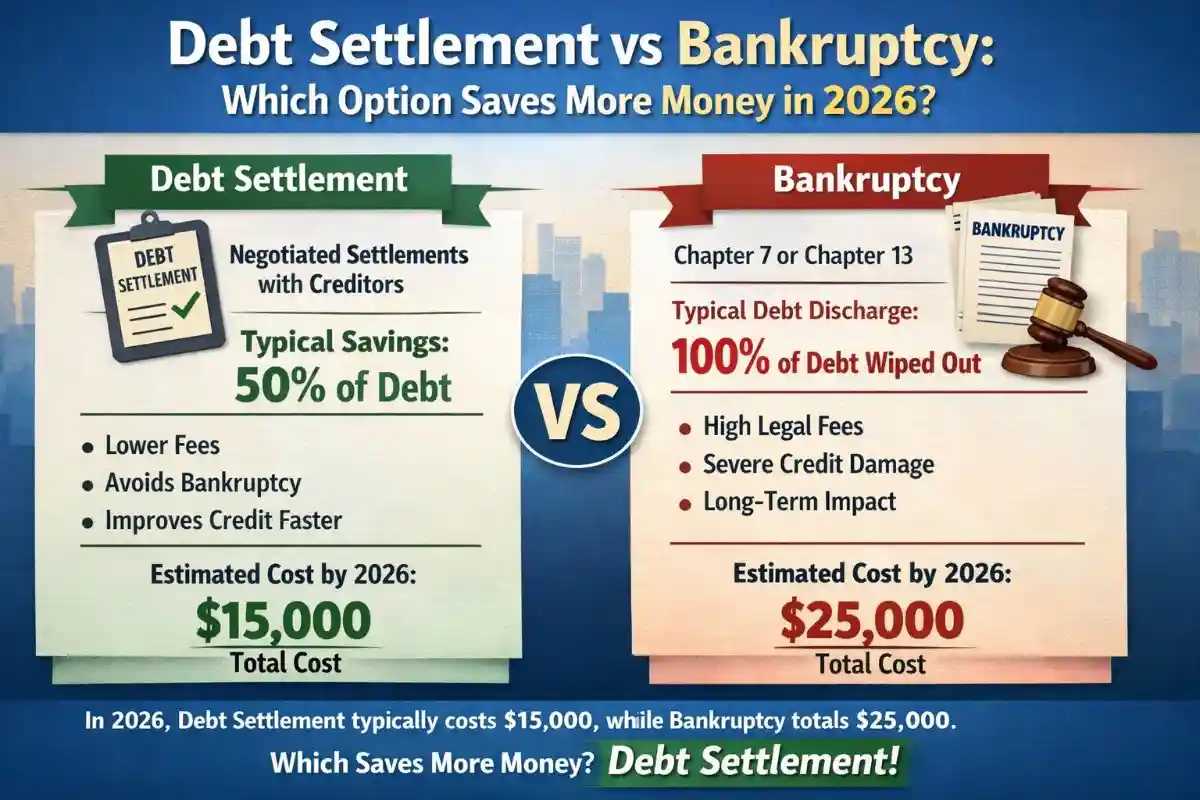
Total Cost Analysis: Which Saves More?
Example Scenario: $50,000 Credit Card Debt
Debt Settlement
- Settlement at 50%: $25,000
- Company fees (20%): $10,000
- Total paid: ~$35,000
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- Attorney & filing fees: ~$2,500
- Debt discharged: $50,000
- Total paid: ~$2,500
In purely financial terms, Chapter 7 often saves more money if you qualify.
Credit Score Impact in 2026
Both options severely impact your credit score initially.
- Debt settlement: Accounts marked as "settled for less"
- Chapter 7: Bankruptcy public record for 10 years
- Chapter 13: Bankruptcy public record for 7 years
However, many consumers begin rebuilding credit within 12–24 months after discharge.
Legal Protection Differences
Debt settlement does NOT guarantee protection from:
- Lawsuits
- Wage garnishments
- Bank levies
Bankruptcy provides immediate federal court protection through the automatic stay.
Tax Consequences in 2026
Forgiven debt through settlement may be considered taxable income (IRS Form 1099-C). This could create an unexpected tax bill.
Bankruptcy discharge is generally NOT taxable.
Who Qualifies for Chapter 7?
Eligibility depends on passing the means test, which compares your income to your state’s median income level.
High-income earners may be directed to Chapter 13 instead.
When Debt Settlement May Be Better
- You do not qualify for Chapter 7
- You want to avoid bankruptcy record
- You have moderate debt ($10K–$30K)
- You can accumulate lump-sum payments
When Bankruptcy May Be Better
- Debt exceeds $30,000–$40,000
- You face lawsuits or garnishment
- You have limited assets
- You need fast relief
Asset Protection Considerations
Chapter 7 may require liquidation of non-exempt assets, though many filers keep primary residences and vehicles under exemption laws.
Debt settlement does not involve court supervision of assets.
Emotional & Psychological Factors
Debt stress affects mental health, relationships, and productivity. Bankruptcy often provides immediate emotional relief due to legal protection.
Alternatives to Consider
- Debt consolidation loans
- Balance transfer credit cards
- Credit counseling programs
- Negotiating directly with creditors
How Long Until You Can Buy a Home Again?
| Event | FHA Loan Waiting Period | Conventional Loan Waiting Period |
|---|---|---|
| Chapter 7 | 2 Years | 4 Years |
| Chapter 13 | 1 Year (with approval) | 2–4 Years |
| Debt Settlement | 2–4 Years | Varies |
Final Verdict: Which Saves More Money in 2026?
If you qualify for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, it typically saves more money and resolves debt faster than settlement — especially for large unsecured balances.
Debt settlement may be appropriate for moderate debt levels or individuals seeking to avoid a public bankruptcy record.
The best choice depends on:
- Total debt amount
- Income level
- Asset ownership
- Lawsuit risk
- Long-term financial goals
Consulting a qualified bankruptcy attorney or certified debt specialist before making a decision is strongly recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does debt settlement hurt your credit?
Yes, missed payments and settlements negatively impact credit scores.
Can bankruptcy eliminate all debt?
Most unsecured debts are dischargeable, but student loans and certain taxes usually are not.
Is bankruptcy public record?
Yes, but practical visibility varies.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Laws vary by state and individual circumstances. Consult a licensed bankruptcy attorney for personalized guidance.